Introduction
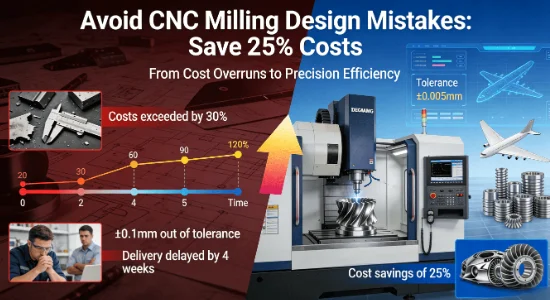
Many manufacturing projects in high-stakes industries like aerospace and automotive face significant overruns in cost and timeline due to overlooked design flaws in the CNC milling phase. The root cause often lies not in the machining itself, but in the upstream design process, where a lack of standardized geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) principles leads to parts that are difficult, expensive, or impossible to manufacture correctly the first time.
This article provides a data-driven framework, grounded in international standards like ASME Y14.5 and ISO 9001, to help engineers and designers avoid common pitfalls, optimize part designs, and achieve substantial cost savings while ensuring uncompromised quality and reliability.
What Is CNC Milling and How Does It Work?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling is a subtractive manufacturing process where pre-programmed computer software dictates the movement of factory tools and machinery. It transforms a solid block of material into a complex part by removing material with high-speed rotating cutters. The process begins with a 3D CAD model, which is translated into a set of instructions (G-code) for the CNC machine to follow, controlling everything from toolpath and spindle speed to feed rate.
1. The Digital Workflow: From CAD to Finished Part
The journey starts with Computer-Aided Design (CAD), where the part’s geometry is defined. This model is then imported into Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software, which generates the precise toolpaths and G-code. Critical to this stage is applying the correct GD&T principles, as defined by standards like ASME Y14.5, to specify tolerances, datums, and other critical features that ensure the part’s form, fit, and function.
2. The Role of Multi-Axis Machining Kinematics
While basic 3-axis milling moves the cutter along linear X, Y, and Z axes, advanced machines offer additional rotational axes (e.g., A, B, or C). This capability allows the tool to approach the workpiece from virtually any angle in a single setup. This dynamic tool orientation is fundamental for creating complex geometries without the cumulative errors introduced by manually repositioning the part multiple times.
3. Achieving Precision Through Controlled Material Removal
The essence of milling is precision material removal. Factors like cutter selection, step-over distance, and chip load are meticulously calculated. The goal is to achieve the desired surface finish and dimensional accuracy efficiently, minimizing secondary operations. Properly programmed, CNC milling can hold tolerances as tight as ±0.005 mm, making it indispensable for precision components.
How Does 5-Axis Milling Enhance Precision for Complex Parts?
Traditional 3-axis machining hits a wall with parts featuring deep cavities, undercuts, or contoured surfaces. 5-axis CNC machining overcomes these limitations by enabling simultaneous movement along five axes, allowing the cutting tool to maintain the optimal orientation to the workpiece surface throughout the operation.
- Eliminating Cumulative Error with Single-Setup Machining: The most significant advantage is the elimination of multiple setups. In 3-axis machining, each time a part is repositioned, a new datum is established, introducing potential misalignment. 5-axis machining completes the part in one fixture, ensuring all features are machined relative to a single datum. This inherently enhances geometric accuracy and is crucial for adhering to the stringent tolerances required by ASME Y14.5.
- Overcoming Geometric and Tool Accessibility Challenges: With its two rotational axes, a 5-axis machine can tilt the tool or workpiece to reach areas that are inaccessible with a straight vertical approach. This eliminates the need for complex custom fixtures and allows for the machining of a monolithic part where a 3-axis process would require designing multiple components for later assembly. This not only improves strength but also reduces assembly time and cost.
- Improving Surface Finish and Tool Life: By allowing the use of shorter, more rigid cutters and enabling flank milling (using the side of the tool) instead of less efficient point milling, 5-axis machining produces superior surface finishes on contoured surfaces. It also promotes longer tool life and higher cutting speeds by maintaining a consistent chip load and optimal cutting angle, leading to greater overall process efficiency.
What Are the Key Materials for CNC Milling and How to Choose Them?
Material selection is a critical cost-performance trade-off. The wrong choice can lead to premature part failure, excessive machining costs, or unnecessary expenses. The selection must balance mechanical properties, machinability, and project budget.
1. Aluminum Alloys: The Standard for Prototyping and Lightweight Parts
Aluminum alloys like 6061 and 7075 are popular for their excellent strength-to-weight ratio, good corrosion resistance, and superb machinability. They are often the go-to choice for aerospace frames, automotive components, and rapid prototyping because they allow for faster machining speeds, reducing production time and cost.
2. Stainless Steels and Titanium: For High-Strength, Corrosion-Resistant Applications
For applications demanding high strength, durability, and resistance to extreme temperatures and corrosion, stainless steel (e.g., 304, 316) and titanium alloys (e.g., Grade 5, Ti-6Al-4V) are indispensable. While more challenging and costly to machine, they are essential for surgical implants, aerospace engine components, and high-performance automotive systems.For in-depth guidance on material selection, please refer to the professional precision CNC milling services blog.
3. Engineering Plastics and Composites for Specialized Needs
Materials like PEEK, Ultem, and carbon fiber composites offer unique properties such as high chemical resistance, electrical insulation, and low density. Machining these materials requires specific tooling and parameters to prevent delamination or heat deformation, but they are ideal for specific aerospace, automotive, and medical applications.
How Can CNC Milling Solve Challenges in Aerospace Manufacturing?
The aerospace industry demands the highest levels of performance reliability and lightweight optimization, all while complying with rigorous safety and quality standards. CNC milling, particularly 5-axis technology, is at the core of meeting these challenges.
1. Mastering Complex Aerodynamic Geometries
Aircraft components like turbine blades, wing ribs, and ducting require complex, organic shapes that are often impossible to produce with conventional methods. 5-axis CNC machining enables the precise creation of these aerodynamic profiles from a single piece of metal, ensuring structural integrity and optimal performance.
2. Implementing Rigorous Quality Control and Traceability
Aerospace manufacturing is governed by standards like AS9100D, which builds upon the quality management principles of ISO 9001. This means every milled part undergoes strict in-process and final inspections using CMMs (Coordinate Measuring Machines) and other metrology tools. All data is documented for full traceability, which is non-negotiable for safety-critical components.
3. Achieving Lightweighting Through Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
A key driver in aerospace is reducing weight without sacrificing strength. Through advanced DFM analysis, engineers can design parts with thin walls and complex internal structures that are only feasible with 5-axis milling. This approach, often called “lightweighting,” directly contributes to improved fuel efficiency and payload capacity.
What Quality Control Measures Ensure High-Performance CNC Milled Parts?
Investing in advanced machinery is futile without a robust Quality Management System (QMS). A systematic approach to quality control is what separates a reliable supplier from a risky one.
- In-Process Monitoring and Closed-Loop Systems: Modern CNC mills can be equipped with on-machine probing systems that measure critical dimensions during or after machining. This real-time data is fed back to the machine control to automatically compensate for tool wear or thermal drift, creating a closed-loop manufacturing process that maintains tolerances consistently and reduces scrap.
- Final Inspection Against Digital Twins: After machining, parts undergo a final inspection, often using a CMM. The part is measured against its original CAD model (the “digital twin”), and a detailed deviation report is generated. This verification is essential for ensuring compliance with the specified GD&T callouts and final part approval.
- The Role of Certifications like ISO 9001:2015: A manufacturer’s adherence to international standards like ISO 9001:2015 is a strong indicator of a mature QMS. This certification demonstrates a commitment to continuous improvement, structured processes, and documented procedures, ensuring that quality is baked into every step of the workflow, from order to delivery.
How to Select a CNC Milling Service Provider for Cost-Effective Projects?
Choosing the right CNC milling service is just as important as the design itself. An ideal supplier can be an extension of your engineering team, providing not only machining services but also valuable expertise.
1. Evaluate Technical Capabilities and Technology Stack
Look for a provider with a range of equipment, including multi-axis CNC mills, and advanced CAM software. Their ability to handle your specific material and geometry requirements is paramount. Don’t hesitate to ask about their experience with similar projects in your industry.
2. Scrutinize Their Quality Management and Certifications
Always verify certifications. ISO 9001 is a baseline, while industry-specific certifications like AS9100D for aerospace or ISO 13485 for medical devices show a deeper commitment to sector-specific requirements. This due diligence mitigates risk and ensures compliance.
3. Assess Their DFM Feedback and Communication
A top-tier supplier will provide a comprehensive Design for Manufacturability (DFM) analysis with your quote. This feedback, which suggests optimizations for cost, durability, and manufacturability, is invaluable. Transparent and proactive communication throughout the project is a hallmark of a reliable partner.
Conclusion
Avoiding costly CNC milling design mistakes requires a proactive approach that integrates advanced manufacturing principles with rigorous design standards from the very beginning. By understanding the capabilities of 5-axis machining, selecting materials wisely, and partnering with a quality-focused supplier, engineers in the aerospace and automotive sectors can significantly reduce production costs, accelerate time-to-market, and achieve a level of precision and reliability that meets the highest industry demands.
FAQs
Q: What is the typical tolerance achievable with CNC milling?
A: High-precision CNC milling can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.005 mm, depending on material and machine capabilities. This ensures parts meet stringent industry standards, such as those in aerospace.
Q: How does 5-axis milling differ from 3-axis milling?
A: 5-axis milling allows simultaneous movement along five axes, enabling complex geometries and reduced setup times, whereas 3-axis is limited to simpler shapes. This enhances efficiency for parts like turbine blades.
Q: What materials are best for high-strength CNC milling applications?
A: Materials like titanium alloys and stainless steel offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios, ideal for automotive and aerospace sectors. Selection depends on factors like corrosion resistance and cost.
Q: How long does it take to get CNC milled parts from prototype to production?
A: Lead times vary, but rapid prototyping can take 1-3 days, while production batches may require 1-2 weeks. Advanced providers optimize scheduling to minimize delays.
Q: What certifications should I look for in a CNC milling service provider?
A: Key certifications include ISO 9001 for quality management and AS9100D for aerospace, ensuring adherence to international standards and reliable part performance.
Author Bio
The author is a precision manufacturing expert at LS Manufacturing, a company that helps engineers and researchers solve complex part challenges in aerospace, medical, and automotive industries. With certifications such as IATF 16949 and AS9100D, the team ensures high-quality solutions through advanced technologies. For more insights, Contact them Todayfor a free, no-obligation project review and DFM analysis. Turn your concept into a cost-effective reality.